It is an age-old Aussie tradition to give all things a fair go, and this tradition has not been abandoned in the education system as well. The dichotomy between vocational skills and academic excellence has long been debated within the regime of the modern education system. Should the students be pushed towards academic prowess and encouraged to secure high grades in traditional subjects? Or should they be empowered to master the practical trades as well? We reckon it’s all about striking the perfect balance and the Australian education system has nailed this balance with its fresh take. So how does the Australian education system work? Let’s find out!

Australian Educational System: A Brief Overview
Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF)
The Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF) implemented in 1995 injects a unique factor into the Aussie educational system. It specifies the standards of qualifications for the tertiary education sector (higher education, vocational education, and training) in addition to the school leaving certificate, called the Senior Secondary Certificate of Education. There are 10 levels within this AQF framework which interconnects the different schools, colleges, and universities in a single national system. Let’s have a look at the levels-
- Level 1- Certificate I
- Level 2- Certificate II
- Level 3- Certificate III
- Level 4- certificate IV
- Level 5- Diploma
- Level 6- Advanced Diploma
- Level 7- Bachelor Degree
- Level 8- Bachelor Honours Degree
- Level 9- Master’s Degree
- Level 10 – Doctoral Degree
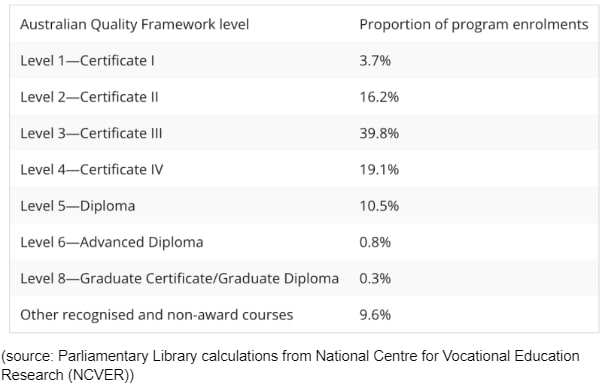
So, while schooling is compulsory in Australia, it is up to the students to decide whether they want to continue to pursue a schooling degree or a non-schooling degree as a part of their higher education. Interestingly, the majority of the population recognise the importance of practical, hands-on learning and hence opts for non-schooling diplomas. In 2022, 63% of the population aged between 15-74 years were reported to have non-school qualifications. The proportion of nationally recognized program enrolments at each level in 2022, as per the Parliament of Australia, is as follows:
The Four-Stage System

Early Childhood Education
The first stage of the Aussie system is Kindergarten aimed at students aged 4-5 years. Early education primarily focuses on making friends, learning to work with others, building communication and cognitive skills, and expressing creativity.
Primary School Education
The primary education stage comprises students aged between 6 to 11 years. At this stage, the schools generally focus on developing essential intellectual, literacy, numeracy, and social-emotional skills. Knowledge about the world around them is also taught.
Secondary School Education
Secondary education under the Australian framework begins for students at the age of 12 and is a seven-year program that students complete at the age of 18. This stage focuses on traditional subjects during the first four years which includes subjects like mathematics, history, language, science, geography, citizenship, civics, arts, etc. However, students have the option at year ten, i.e., at 16 years of age to opt out of these traditional subjects and enroll for Vocational Education and Training (VET). The Senior Secondary Certificate of Education is awarded to those completing their schooling.
Higher Education
The higher education sector in Australia is further divided into two sectors. The first are the universities that are registered by the Tertiary Education Quality and Standards Agency (TEQSA) and the second sector is VET, which is registered and regulated by the Australian Skills Quality Agency (ASQA).
Integration of Academic and Vocational Pathways
The Aussie educational system believes in providing students with the best of both worlds. During the 1990s, Australian senior secondary education, which was previously undertaken exclusively by those pursuing a university pathway, was re-positioned as the minimum level of educational attainment. This was designed to serve the dual purpose of providing entry into further education and training opportunities, as well as preparing young people for entry into the labor market. As a result, students who are pursuing academic subjects also have the opportunity to benefit from vocational training. In the financial year 2022-23, it was reported that 79% of employed people with a non-school qualification had qualification relevant to their current job. This seamless integration of vocational and academic pathways is what sets the Aussie system apart from any other educational system. This method also prevents discrimination among students.

Benefits of A Holistic Pedagogy
The educational ethos in Aussie culture is embedded in the belief that different students have different aspirations, hence, the education should cater to all the diverse aspirations of the students. Over 4.5 million students were enrolled in VET in 2022, representing almost a quarter of the population. This does not mean that Australian education does not recognize the significance of academic achievements, rather, it simply means that the Australian system recognizes that not all students are suited for the path of academic excellence. There are more ways to skin a cat, so to speak. This is why in Australia students are offered top-notch notch programs that not only allow them to flex their mental muscles but also offer a wide range of educational opportunities that include theoretical as well as hands-on training experience.
Nurturing Academic Excellence
Got a young Einstein with natural aptitude in traditional academic subjects? The Aussie education system has got you covered mate! The Australian system provides a nurturing environment to these brilliant minds which enables them to maximise their potential. They are offered enriched learning experiences at school, specially designed for high-performing students which include extension classes, advanced placement programs, and several academic competitions to brush their brilliance alongside their peers. These learning experiences are designed to cultivate critical thinking among students and challenge them to excel in academic fields so that they are equipped with all the necessary skills to reach for the stars.
Embracing Vocational Education and Training (VET)
The Australian educational system is also aware that not all folks are cut out for academic excellence. But that should not be a reason for them to lag behind their peers, instead, they should have equal opportunities for a successful future. Keeping this in mind, the Aussies place a great emphasis on vocational education and training (VET) which provides the students with practical skills that are necessary for a high-demand workforce.
These VET programs offer a wide range of practical skills including information technology, tourism and hospitality, automation and technology, agriculture, fashion, and many more. The three fields of study with the highest proportion of program enrolments in the year 2022, were management and commerce (20.5%), society and culture (18.3%), and engineering and related technologies (17.5%). With these programs, students get to have technical preparation for hundreds of different careers. These courses mostly provide certifications, diplomas, or advanced diplomas. The interesting thing about these programs is that it allow the students to apply for jobs directly without having to complete a university education.
The Future of Education
The Aussie system is all about giving education a fair go. Thus, flexibility is the cornerstone of the educational framework in Australia so that all students can tailor their educational experiences based on their strengths, interests, and aspirations. By prioritizing both academic excellence and vocational skills, Australia equips students with the knowledge, skills, and competencies needed to succeed in a rapidly changing world.



